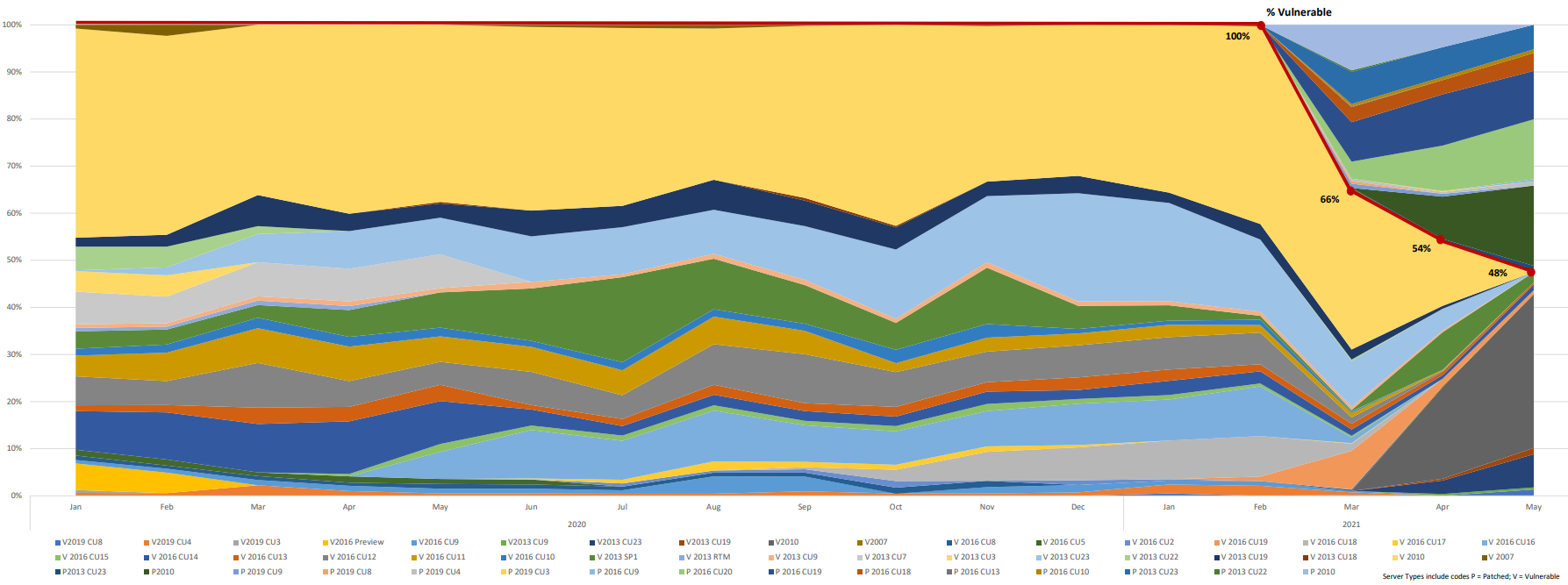
It has been 11 weeks since Microsoft released patched versions of Exchange Server Software, which were being actively exploited due to cybersecurity vulnerabilities since the beginning of 2021. We took a look at our data in mid-April to understand how quickly users were updating their software. The stats were not great. Over 50% of users were still running vulnerable versions of Exchange six weeks after the update release. We gave it another month, hoping that the vast majority of users would have updated their software by then. Unfortunately, that is not the case. Our data shows that 48% of users are still running vulnerable versions of the Exchange software. Exchange Server Software has a cybersecurity vulnerability and updating immediately helps to avoid intrusion, protect against exploits, a loss of data and confidentiality.
According to the Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), “New vulnerabilities are continually emerging, but the best defense against attackers exploiting patched vulnerabilities is simple: keep your software up to date. This is the most effective measure you can take to protect your computer, phone, and other digital devices.”
Cyber criminals are attacking and exploiting everywhere they can, from individual machines to servers of infrastructure giants. It is up to the users to prevent these attacks by being pro-active in securing their devices and data. Follow the guidance from the CISA and prevent attacks by updating your software as soon as the release becomes available.
Exchange Server Software from Microsoft has a cybersecurity vulnerability without patched versions.
Cyber risks exist for users still running vulnerable versions of Exchange Server. The patched versions of Exchange Server fix the Microsoft vulnerability. This provides a good measure of cybersecurity and protection with the updated software installed. Read more about the Exchange Server security issues at A Simple Guide to the Microsoft Exchange 0-day Vulnerabilities (pcmatic.com) We will continue to monitor Microsoft’s Exchange Server Software cybersecurity vulnerability as well as user adoption of the patched versions.