There is nothing more frustrating than trying to work on a sluggish computer. Slow speeds can turn even simple tasks into a headache whether you’re trying to stream a movie, work on a project, or browse the web. The first question is: Is the issue with your computer, or is it your Internet connection? Knowing how to diagnose and solve the problem is essential for getting your system back on track.
In this blog, we’ll walk through several common issues, teach you how to identify whether the problem is your device or your Internet Service Provider (ISP), and how to troubleshoot and fix them.
Signs of a Slow Computer vs. Slow Internet
Before diving into the technical aspects, it’s important to identify whether the sluggish performance is coming from your device or the internet connection. Here are some signs to help:
Slow Computer:
Programs take longer to load, the operating system lags, or the entire system freezes. This could point to issues like hard drive space, too many background programs, or hardware failures.
Slow Internet:
Websites take longer to load, videos buffer frequently, or download speeds are much slower than expected. This could indicate network congestion, ISP problems, or a weak Wi-Fi signal.
Step 1: Check Your Internet Connection
If you suspect that the internet is causing your issues, the first step is to test your internet connection. You can use speed test websites or apps to measure your download and upload speeds. Compare those results to the speeds your ISP promises in your service plan. Check your download and upload speeds, latency, and network jitter with PC Matic’s Internet Speed Test.
Running a Trace Route
A traceroute command can help you identify where network slowdowns occur. Trace route shows the path your internet traffic takes to reach a server and where delays or “latency” occur. If there’s a significant delay at one of the points, it could mean there’s an issue with your ISP.
Here’s how to run a traceroute on Windows:
1. Open the Command Prompt by searching for it in the start menu.
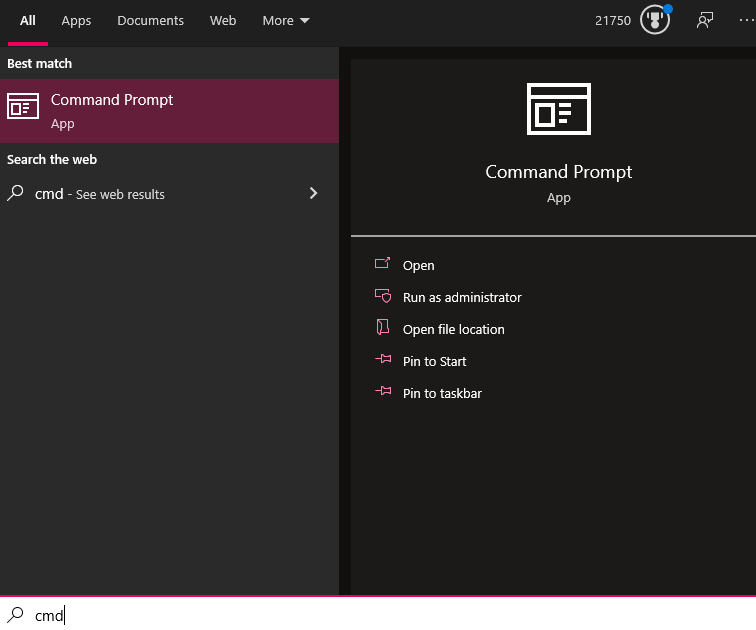
2. Type tracert www.example.com (replace “www.example.com” with the website you’re trying to reach) and hit Enter.
3. The results will show each step your internet traffic takes – if you see a long delay or failure message at one of the “hops,” that might indicate an issue with your ISP.
If you find that the issue is not with your connection but with your device, let’s move on to troubleshooting your computer. To learn more about running a traceroute, visit Catchpoint.
Step 2: Check the Device
If you’ve ruled out the internet connection, it’s time to look at your computer. Several factors can cause a slow pc, from old hardware to too many programs running in the background.
Check Your CPU Usage with Task Manager
If your computer is running slowly, check your computer’s resource usage. Windows comes with Task Manager and Mac some with Activity Monitor, a built-in tool that allows you to see how your CPU (processor), memory, disk space, and other resources are used.
1. Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc to open Task Manager.
2. Go to the Processes tab to see which applications use the most resources.
3. Sort by CPU, Memory, and Disk to identify resource-hogging programs.
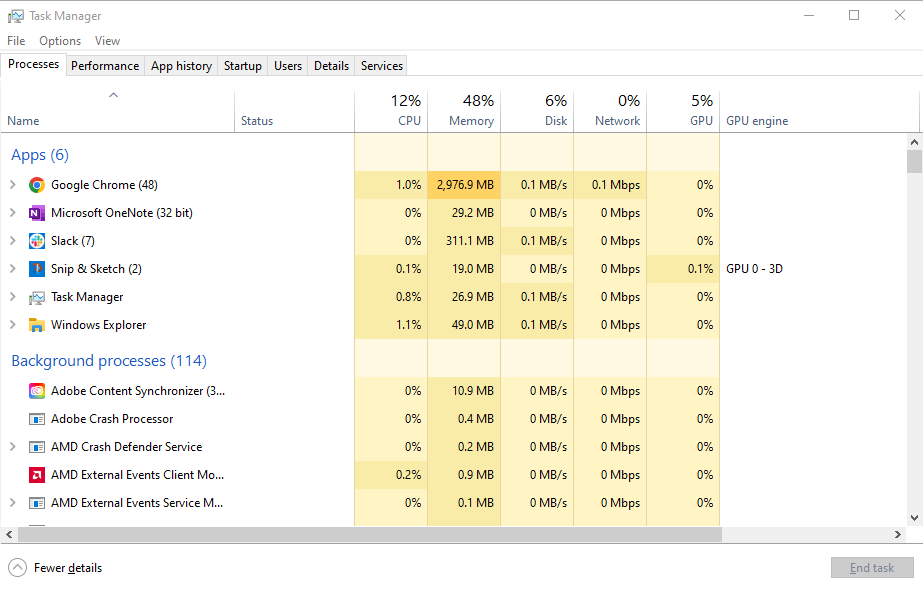
If one program takes up most of your CPU or storage space, consider closing it or uninstalling it if you don’t need it.
Manage Startup Programs
One of the most common reasons for slow computer performance over time is having too many programs launch automatically when you start your system. These programs run in the background, eating up resources like CPU and memory.
To manage startup programs:
1. Open Task Manager (Ctrl + Shift + Esc).
2. Go to the Startup tab.
3. Right-click on any unnecessary programs and select Disable.
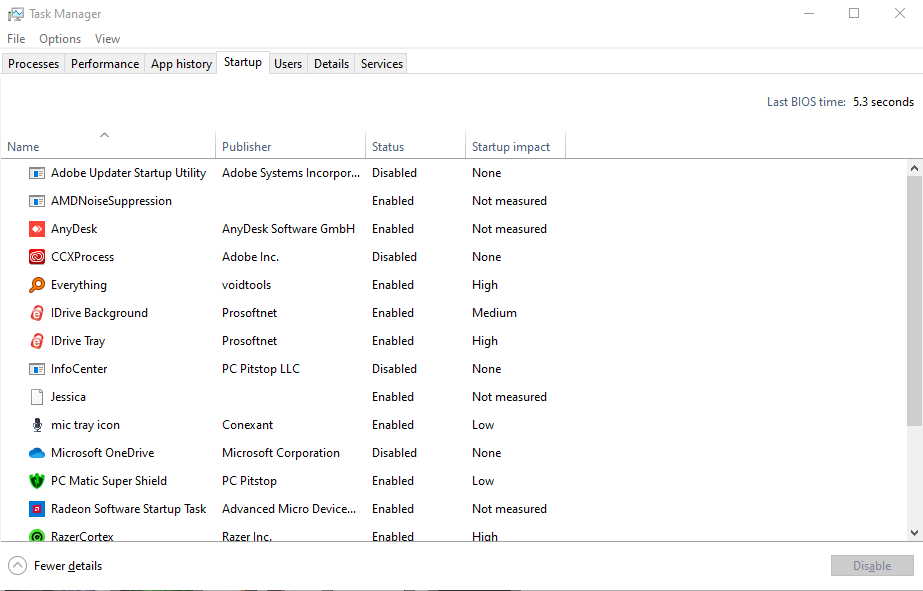
This will prevent these programs from launching the next time you start your computer, freeing up resources and improving performance.
Free Up Disk Space
Running out of disk space can slow down your system considerably. When your hard disk drive (HDD) or solid-state drive (SSD) is too full, it doesn’t have enough room to operate efficiently. You can check your disk space by opening File Explorer, right-clicking on your drive (usually C:), and selecting Properties to see how much free space is left.
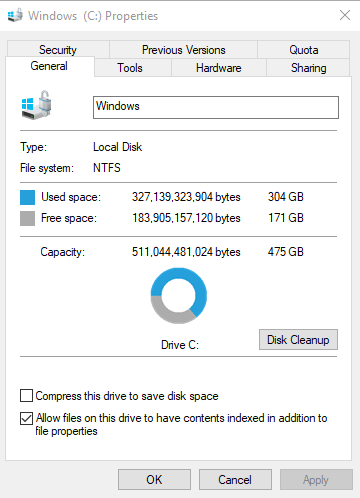
If your disk is near capacity, here are some ways to free up space:
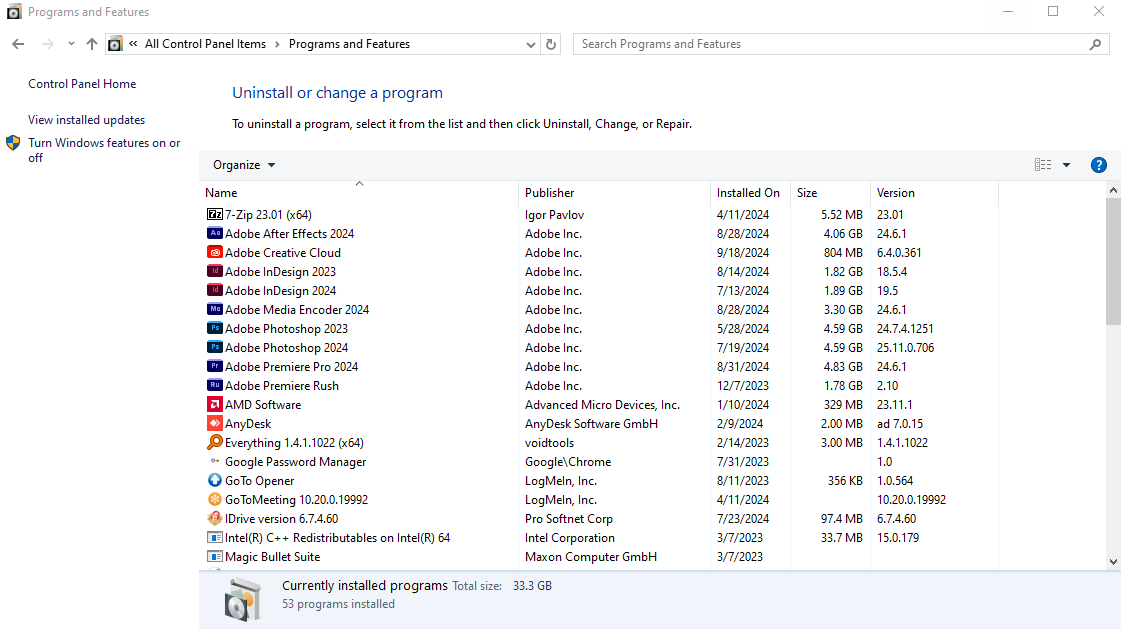
Uninstall unnecessary programs:
Go to Control Panel > Programs and Features, then uninstall any programs you no longer need.
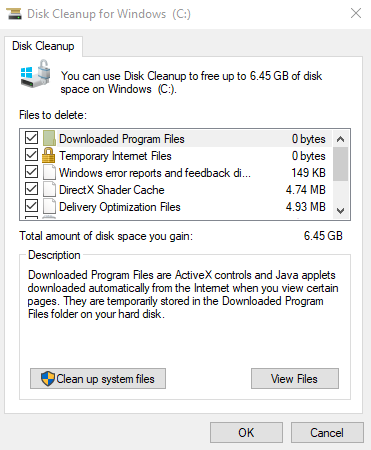
Delete temporary and unnecessary files:
Temporary files can build up over time and take up a lot of space. You can use the Disk Cleanup tool to remove them.
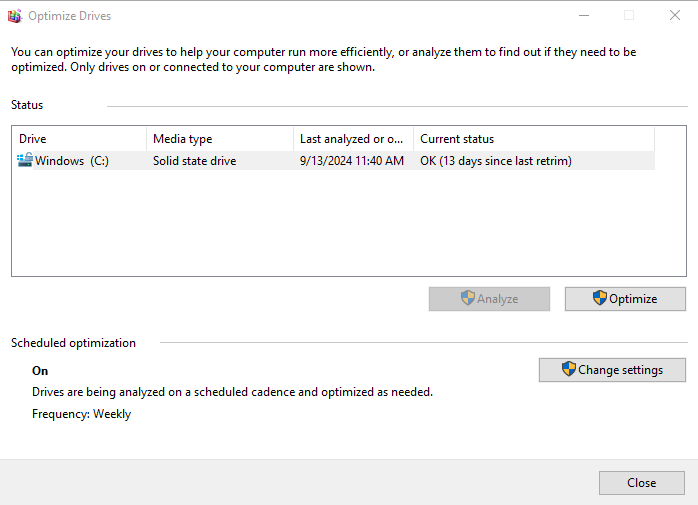
Defragment your hard drive:
You can also run a defrag to reorganize fragmented data and improve performance. Search for “Defragment and Optimize Drives” in the start menu to run the tool.
Empty the recycle bin:
Ensure you regularly empty the recycle bin and permanently delete large files you no longer need.
If you’re still low on space, consider upgrading to a larger SSD, which will also give you a speed boost compared to a traditional HDD.
Step 3: Check for Malware or Viruses
Malware and viruses can significantly slow down your computer. Installing a reputable antivirus program and running regular scans is critical for maintaining system performance. If you already have antivirus software but are still experiencing slow performance, try switching to another program to see if it catches anything missed by the first one.
Symptoms of Malware:
1. Your pc performance is running slow.
2. You experience frequent pop-ups or browser redirects.
3. Programs crash unexpectedly.
If any sounds familiar, run a full system scan with PC Matic.
Step 4: Perform System Updates
Outdated software or operating systems can cause performance issues. Regular software updates not only fix bugs but also include important security patches. If your computer is running slowly, check whether your system is up-to-date.
To check for updates on Windows Updates:
1. Open Settings by clicking the Start menu and selecting the gear icon.
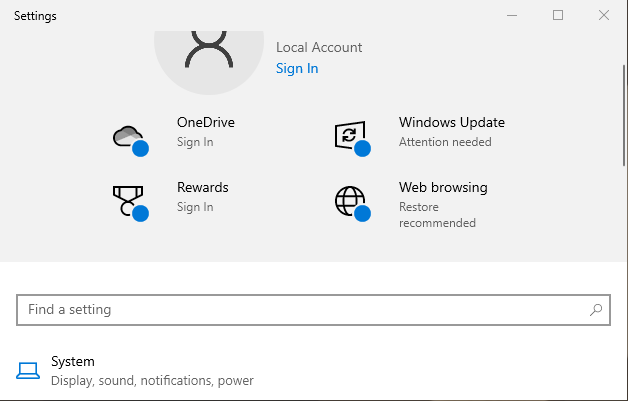
2. Go to Update & Security.
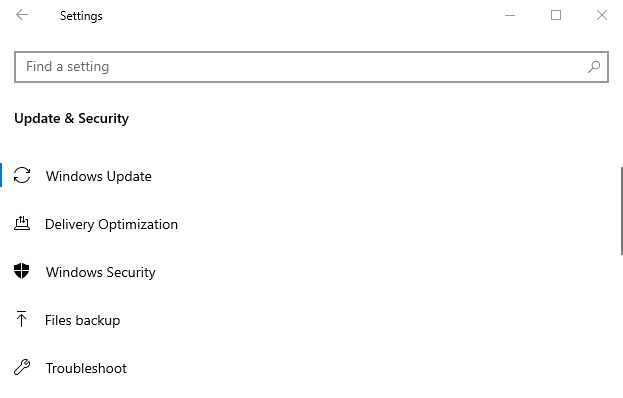
3. Select Check for Updates.
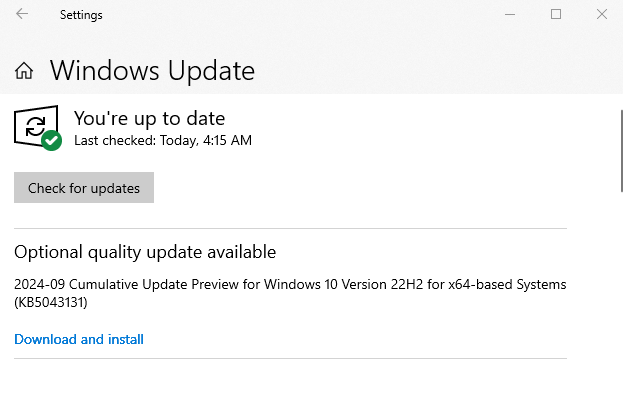
Install any available updates and restart your computer. If your web browser, like Chrome or Edge, is outdated, that could also slow down your browsing experience. Make sure to update your browser regularly, and check to see if it’s running the latest version.
Step 5: Hardware Issues: Overheating or Failing Components
Hardware issues can also slow down your computer. Two common culprits are overheating and failing hardware.
Overheating
If your CPU overheats, it can cause your computer to slow down to protect the hardware. Overheating can be caused by dust buildup or poor ventilation. Here are a few tips to avoid this:
1. Keep the vents on your computer clear and ensure the fans are running smoothly.
2. Use a cooling pad if you’re on a laptop.
3. Regularly clean out dust from the fans and vents.
Failing HDD or SSD
Over time, HDDs or SSDs can wear out. Failing drives might start making strange noises or cause frequent crashes and slowdowns. You can check the health of your drive using built-in tools on Microsoft Windows 11:
1. Open File Explorer.
2. Right-click your main drive (usually C:) and select Properties.
3. Go to the Tools tab and select Check under the Error Checking section.
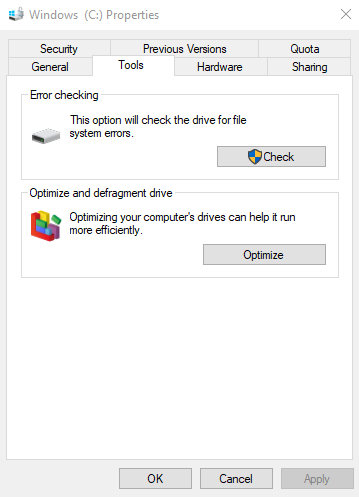
If you notice any issues, it might be time to upgrade your hardware.
Step 6: Maximize Your Computer’s Processing Power
Your computer’s processing power is determined by its CPU and Random Access Memory (RAM). Your computer might slow down if intensive programs and too many tasks are running at once. You can maximize performance by upgrading your RAM or closing resource-heavy applications.
Use Task Manager to monitor your system’s CPU and RAM usage and ensure you’re not overloading your computer with too many open programs.
Step 7: Other Troubleshooting Tips
If none of the above steps seem to resolve the issue, here are a few more things to try:
1. Close browser tabs:
Having too many browser tabs open can consume a lot of memory – close unused tabs.
2. Reboot your computer:
Sometimes a simple reboot can resolve issues caused by temporary glitches or memory leaks.
3. Try another device:
Try connecting to another device if you suspect your internet connection is slow, like a smartphone or tablet, to your network. If both devices experience slow speeds, it’s likely your internet connection.
Conclusion
A slow computer can be caused by various factors, from software issues to hardware problems. By running a traceroute, checking your task manager for resource usage, managing startup programs, cleaning up disk space, checking for malware, and keeping your system up-to-date, you can narrow down the root cause. Whether it’s an issue with your device or your internet connection, these steps will help you get back to peak performance.
Remember, keeping your computer healthy involves regular maintenance and updates, just like taking care of a car. Don’t forget to run anti-malware scans, clean out dust, and look for performance to prevent slowdowns before they start!